Mastaba of Kagemni In Egypt: Overview,Prominent Features,History,Interesting facts
Overview:
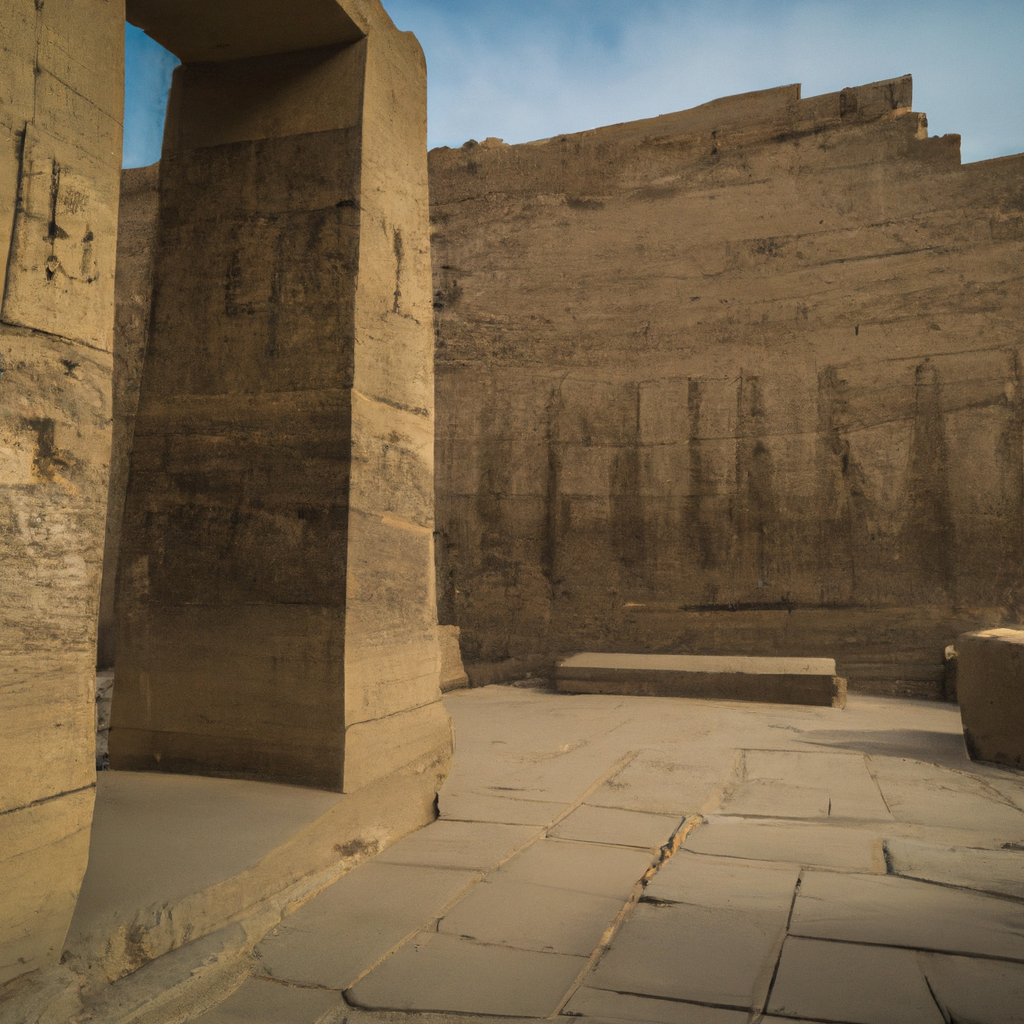
The Mastaba of Kagemni in Egypt is a large ancient Egyptian tomb located in Saqqara, which was built to honor the notable official Kagemni, who was a possible vizier of the Sixth Dynasty Pharaoh Unas. The Mastaba was initiated either at the end of Unas' reign, or just after his death. The Mastaba is notable for its well-preserved columns, exquisite wall decorations, false-doors, and several cartouches of Unas, as well as the Pyramid Texts surrounding them. The Mastaba is characterized by two L-shaped pilots built from wall slabs which form the entrance corridor, and one of the most impressive false door doorframes and reliefs of the Old Kingdom, decorated with images of the god Ptah and the princess Meretites, as well as other important characters from the Sixth Dynasty. Inside, there are dozens of offering-sets and two canopic jars, and several other artifacts belonging to Kagemni. Just beyond the inner door, you'll find the tomb's burial chamber which includes three limestone sarcophagi and two cloth-covered mummy cases. The Mastaba of Kagemni is a highly important archaeological site, as it provides an important insight into the lives and beliefs of Ancient Egyptians from the early Dynastic Period. Its impressive limestone facade and grandiose decorations further demonstrate the enormous wealth and power of Kagemni during his lifetime. It is one of the most beautiful monuments in Egypt
Prominent Features:
- Mastaba was the first type of tomb and was used for prominent figures in Ancient Egypt - Located in the Saqqara area, south of the Cairo plateau - Believed to date to the early 6th dynasty, around 2350 BCE - Constructed from mud-brick - Feature a false door that the spiritual paths of the Pharaoh or the nobles could take - Stone or wooden columns were used to support the roof - Inside the tomb painted scenes depicting everyday life activities and offerings to the gods were found - An offering chamber for the storage of food and other goods was also found You can learn history, culture, and heritage through these magnificent monuments in Egypt.
History:
The Mastaba of Kagemni is a funerary monument located in Saqqara, Egypt, and is one of the oldest known tombs in the history of Ancient Egypt. The Mastaba of Kagemni was built around 3,400 B.C. and is believed to be the tomb of an Old Kingdom official, Kagemni. It is a simple rectangular structure with an entrance built over a stairway. Inside the tomb are a series of chambers, including a serdab, offering chamber, and a false door. The Mastaba of Kagemni is known for its well-preserved wall reliefs, which contain timeless stories of ancient Egyptian life, such as the daily tasks of Egyptian craftsmen, and the symbolic representation of how an afterlife was seen by the Egyptians in this time period. The reliefs also capture scenes of religious rituals, featuring figures of gods and goddesses, as well as images of ships and bulls as symbols of power. The mastaba also holds one of the earliest known hieroglyphic inscriptions in Egypt, written in columns on the walls of the serdab. This inscription is thought to be a hymn to the afterlife. This helps scholars understand early Egyptian beliefs in the afterlife and what they believed would happen when they died. As one of the earliest known tombs in Ancient Egypt, the Mastaba of Kagemni provides insight into the beliefs and customs of the Ancient Egyptians. It is an important archaeological site and a well-preserved reminder of Ancient Egyptian culture and history. Visit one of the famous monuments of Egypt with your friends and family.
Interesting facts:
1. The Mastaba of Kagemni is one of the oldest monuments in ancient Egypt. It is located in the necropolis of Saqqara, south of Cairo, and dates back to the reign of Pharaoh Djedkare Isesi (2323-2291 BC). 2. Kagemni was a vizier to Pharaoh Djedkare Isesi in the Fifth Dynasty of the Old Kingdom. His mastaba, inscribed with his name, is the largest of its kind known from the period. 3. The structure consists of two levels, with an internal burial chamber, and it originally stood approximately 32 ft high. It was covered with a thick layer of white plaster, which has enabled the scenes that decorated the walls, including offering-bringers, people carrying staffs and boats, to be seen today. 4. Scholars believe that these scenes suggest a close connection to the Hymn to the Nile, which describes the bounty generated by the Nile’s annual flood. The original paintings were further decorated with blue and red paint, which add a bright and vibrant element to the ancient artistry. 5. The Mastaba of Kagemni contains a number of architectural innovations, such as an entrance hall with an awning, lined passages with mud-brick walls, and multiple rooms which were used for storage or specific activities. It is thought to have been a luxurious residence, or even a temple complex for the living relatives of Pharaoh Djedkare Isesi. 6. The remains of a pyramid, which was likely connected to the site, were discovered in the 1980s. It is believed that this served as an offering place for religious festivities. 7. The Mastaba of Kagemni was first explored in the late 19th century by French Egyptologist Jacques de Morgan. In the 2000s, a team of archaeologists from Deutsches Archäologisches Institut in Berlin carried out extensive excavations on the monument. One of the historical monuments of Egypt, it tells the story of a bygone era
Explore Egypt most popular tourist destination with us. Mastaba of Kagemni In Egypt: Overview,Prominent Features,History,Interesting facts,which is 35.14 km away from Egypt main town, is the most popular destination to add in your travel wishlist.
-
City:
Egypt
-
state:
Saqqara
-
country:
EG
-
country code:
Egypt
- postcode:
Location:
Saqqara EG