Mastaba of Ankhmahor at Saqqara In Egypt: Overview,Prominent Features,History,Interesting facts
Overview:
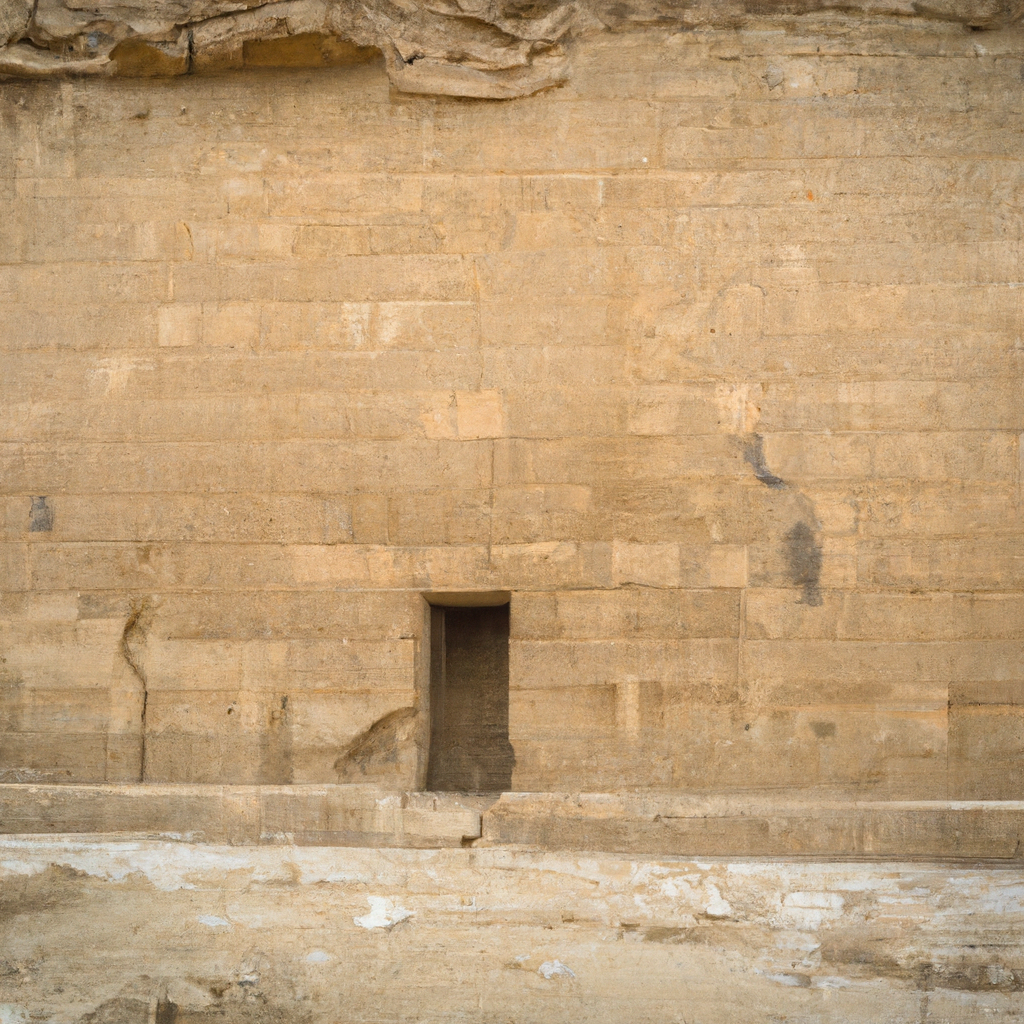
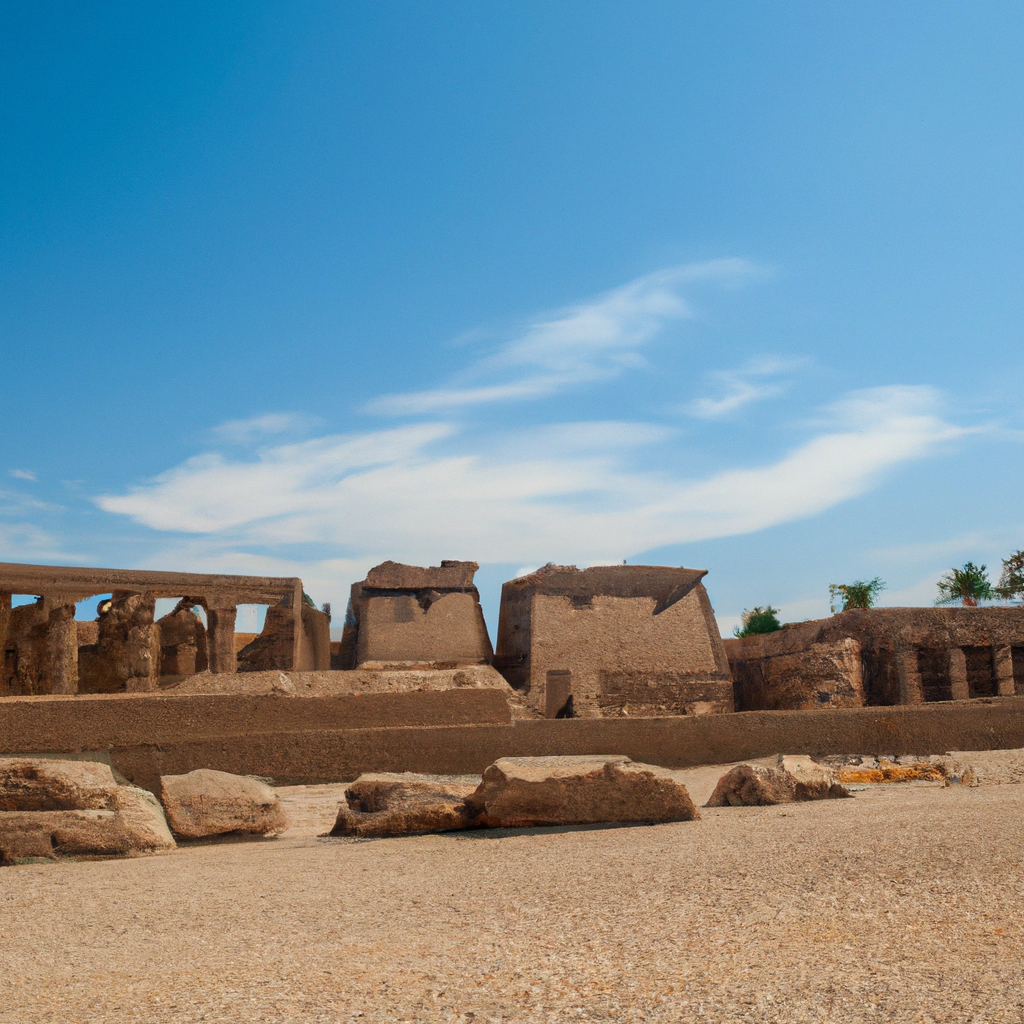
The Mastaba of Ankhmahor is a mud-brick tomb located in the necropolis of Saqqara in Egypt. This Ancient Egyptian funerary monument was likely constructed during the late-Third Dynasty, sometime between 2630 and 2515 BCE. The mastaba belonged to a small gentleman in the court of the Pharaoh Pharaoh Djoser, named Ankhmahor, who served as a supervisor of the Royal Scribes and Physician. The structure includes a chapel, several galleries and a serdab, or a small chamber containing a statue believed to depict Ankhmahor. The facade of the tomb is particularly notable, with its rows of recessed niches leading to the chapel. Inside the mastaba, archaeologists discovered a number of artifacts and inscriptions, which reveal information about Ankhmahor's life prior to his death and the period of time it took to construct his tomb. The well-preserved state of the structure has allowed scholars to learn more about the liturgical customs, architecture, and artwork of one of Ancient Egypt's most significant dynasties. It is one of the most beautiful monuments in Egypt
Prominent Features:
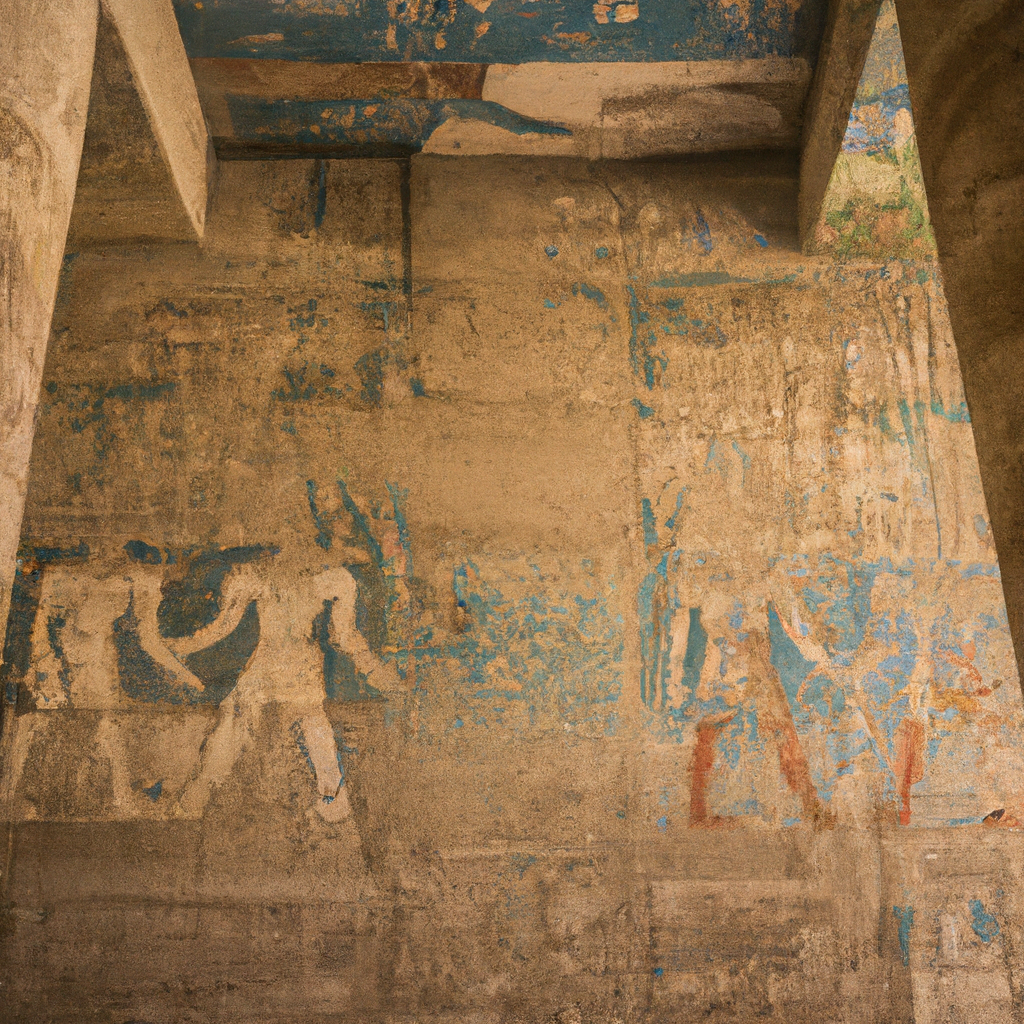
The Mastaba of Ankhmahor at Saqqara is an impressive ancient Egyptian architectural structure located in Saqqara, a large necropolis near Memphis, Egypt. The tomb was constructed during the 6th Dynasty of the Old Kingdom, around 2,500 B.C., and was extensively restored in the 20th century. It was built for Ankhmahor, one of the high-ranking officials of the court of Pharaoh Pepi II. The mastaba complex consists of two sections -- a small portion uncovered by an excavation in 1897 and a much larger part which was discovered later. The tomb consists of several rooms made up of mud brick walls decorated with wonderfully vivid scenes of everyday life from Ancient Egypt. These scenes feature everyday life such as the harvesting of crops, music making, boating, hunting, fishing, and baking, as well as more special occasions like banquets, religious offerings and sacrifices. Along with these well-preserved scenes, the mastaba also features other architectural features such as a pyramid-shaped entranceway, a courtyard, and a portico with an open space. The surrounding area of the site includes a large garden which houses numerous plants and flowers, making it an ideal spot for relaxation and a great way to learn more about Ancient Egypt. You can learn history, culture, and heritage through these magnificent monuments in Egypt.
History:
The Mastaba of Ankhmahor is an ancient Egyptian tomb located in Saqqara, a necropolis located in the area of Memphis. Built around 2400 B.C.E during the reign of Pharaoh Pepi I, the mastaba is the tomb of Ankhmahor, a high-ranking priest in ancient Egypt, who served as the vizier (chief minister) under the Pharaoh. The vast mastaba is renowned for its exquisite decorations and reliefs, which vividly illustrate the life of Ankhmahor and his family and offer interesting insight into ancient Egyptian society. The tomb is unique in that it is the first large painted tomb from the Old Kingdom period. It consists of a large rectangular superstructure with a central chapel, surrounded by a collection of eight subsidiary chapels connected by two long corridors. Inside the chapel are four painted panels depicting Ankhmahor and his family alongside various gods and priestly figures. These paintings are especially notable due to their high degree of detail and vibrant colors. Outside the chapel, visitors can find a variety of brightly-colored reliefs, which depict scenes from Ancient Egyptian mythology, including the journey of Ankhmahor to the afterlife. Additional reliefs depicting the everyday lives of Ankhmahor and his family can be found in the corridors. The Mastaba of Ankhmahor remains an important archaeological site today and is a popular tourist destination. It provides a fascinating insight into Ancient Egyptian culture, and the intricately detailed murals and reliefs continue to amaze visitors from around the world. Visit one of the famous monuments of Egypt with your friends and family.
Interesting facts:
1. The Mastaba of Ankhmahor at Saqqara is the only surviving mastaba from the 6th Dynasty, a period of ancient Egyptian history that lasted from 2345 to 2150 BC. 2. It is the oldest intact building in Saqqara and one of the earliest examples of an Egyptian funerary monument. 3. The mastaba is huge, measuring some 13 meters high and 57 meters wide. 4. Inside the structure are a number of hieroglyphs, which have allowed researchers to piece together some basic information about the afterlife beliefs held by the ancient Egyptians. 5. There are also several reliefs which depict the afterlife and the importance of maintaining a good name in the afterlife. 6. The mastaba contains two false doors which symbolize the opening from this world to the afterlife. 7. The mastaba was constructed from limestone, mud-brick and wood; all of which are materials commonly used in the construction of ancient Egyptian monuments. 8. The burial chamber contained 83 pieces of jewellery, 70 funerary objects, 15 spoons and maces, and a large sarcophagus. One of the historical monuments of Egypt, it tells the story of a bygone era
Explore Egypt most popular tourist destination with us. Mastaba of Ankhmahor at Saqqara In Egypt: Overview,Prominent Features,History,Interesting facts,which is 35.14 km away from Egypt main town, is the most popular destination to add in your travel wishlist.
-
City:
Egypt
-
state:
Saqqara.
-
country:
EG
-
country code:
Egypt
-
postcode:
13512
Location:
Saqqara. EG