Zhoukoudian Archaeological Site In China: Overview,Prominent Features,History,Interesting facts
Overview:
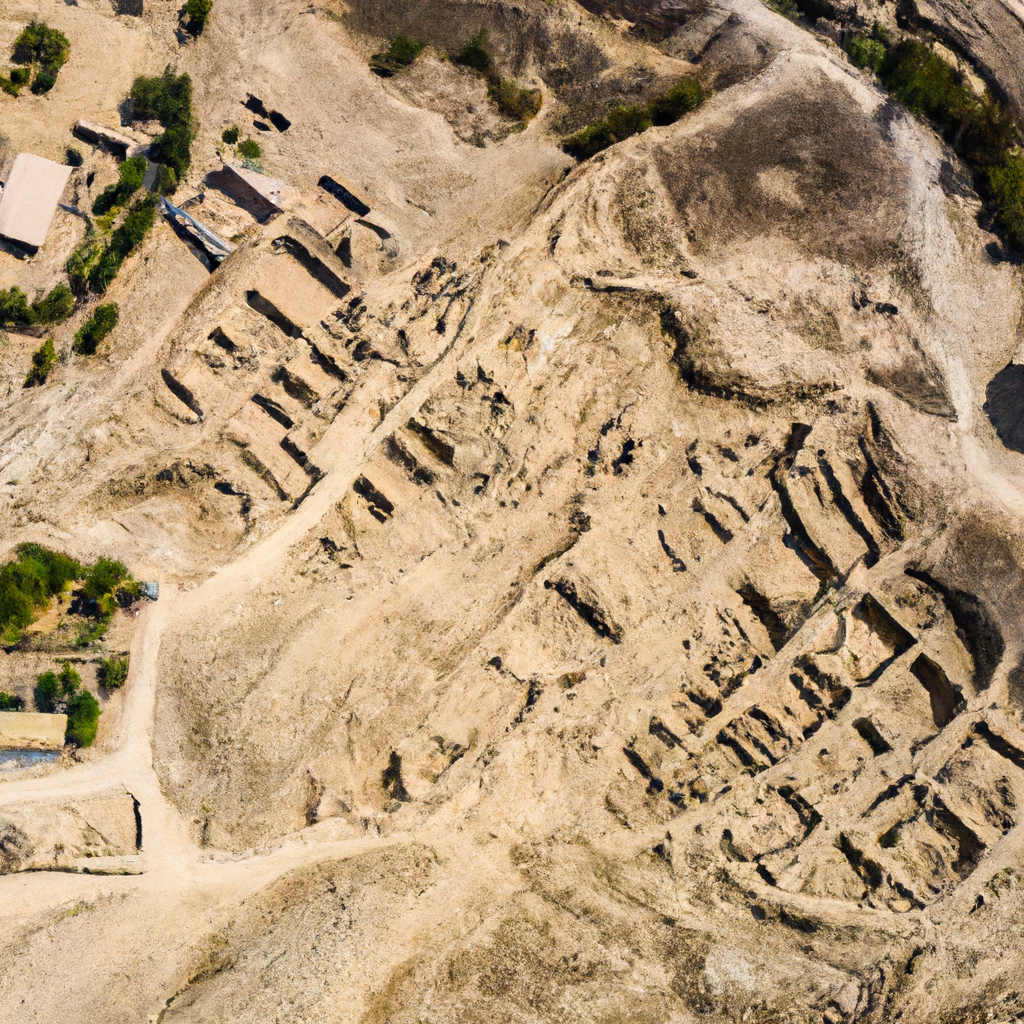
The Zhoukoudian Archaeological Site in China is an important archaeological site located near the city of Beijing, in what is now known as East China. It is best known for the discovery of the earliest known specimens of the genus Homo. This site is considered to be representative of the transitional period between Homo erectus and Homo sapiens. Excavations from this site first began in 1921 and continues until the present day. It is believed to have been inhabited during the Lower and Middle Pleistocene Epochs (780,000-125,000 years ago), and discoveries from the site include abundant assemblages of hominin fossils, animal fossils, lithic artifacts, and numerous other remains. These artifacts and the fossils found on site suggest that the area was home to some of the first known Homo sapiens, and the first settlers of northeast Asia. Zhoukoudian is seen as a unique site in terms of both its intrasite variation and its long-term stratigraphic samples. Concentrated at the site are limestone caves with various cultural deposits, such as two fire-stone hoards. In all, over 40 archaeological deposits containing hominid remains have been identified, including mainly Homo erectus, but also Homo sapiens. The research conducted at Zhoukoudian shows us a great amount of information about the behavior, adaptation, and social life of these early humans. It is one of the most beautiful monuments in China
Prominent Features:
1. UNESCO World Heritage Site: The Zhoukoudian Archaeological Site was declared a UNESCO World Heritage Site in 1987 due to its significant contributions to our understanding of pre-historic human behavior and development. 2. Peking Man: The site is most famous for the discovery of Homo erectus, famously known as Peking Man, by paleontologist Davidson Black in 1927. 3. Ancient Cave Systems: The archaeological site consists of several ancient cave systems, as well as their contents and artefacts. These include stone tools, animal remains, Chinese pottery, and other objects from the Paleolithic, Neolithic, and Bronze ages. 4. Significant Finds: The site has yielded some of the earliest evidence of human activities in East Asia, as well as the longest continuous record of human occupation of any site in China. It has also provided valuable insight into the evolution of Homo erectus and other human species. 5. Conservation Efforts: The Chinese government has taken steps to conserve the site, including restoration work on important buildings at the site and the creation of a nature conservation area for endangered species. You can learn history, culture, and heritage through these magnificent monuments in China.
History:
The Zhoukoudian archaeological site in China is located approximately 50 kilometers south of Beijing in the province of Hebei. It is a limestone cave system that was first investigated by Swedish geologist Johan Gunnar Andersson in 1921-22. The archaeological finds made in the caves, known as the Peking Man Sites, are some of the most significant finds of Homo erectus of the 20th century. The first evidence of human activity at the Zhoukoudian was discovered in the form of scattered human bones, stone tools, and animal bones. Subsequent excavations conducted by Dr. Black between 1921 and 1922 revealed the first skull and jaw of Peking Man. Through further excavations conducted by Dr. Davidson Black, Franz Weidenreich and, later, Pierre Teilhard de Chardin, many other fossils and artifacts have since been unearthed from at the site. The Zhoukoudian archaeological site is an important archaeological find for the study of human evolution and one of the most important sites in China. The site has provided invaluable evidence to scientists on the physical features and lifestyles of humans between 300,000 and 600,000 years ago. In 1987, the site was declared a UNESCO World Heritage Site. The findings at the Zhoukoudian site have been significant for research on Chinese prehistory, as well as, the evolution of Homo erectus. It has helped to understand the human development long before the appearance of modern humans in the region. Visit one of the famous monuments of China with your friends and family.
Interesting facts:
1. Zhoukoudian is one of the most important prehistoric archaeological sites in East Asia, showcasing some of the earliest and most remarkable evidence of early human habitation in the region. 2. The site was first discovered in the late 1920s and is home to layers of Paleolithic and Neolithic remains, including tools, pottery and human bones. 3. In 1929, a jawbone and teeth were discovered at the site that represented a species of extinct hominid, and is now known as Peking Man (Sinanthropus Pekinensis). 4. The human remains and stone tools found in the area demonstrate a long human habitation, and the earliest tools date back 800,000 to 600,000 years ago. 5. The microlithic stone tools found on site have been believed to be the oldest of their kind in East Asia, and the first agricultural tools were found here in 1909. 6. Zhoukoudian is also home to many prehistoric fauna, which include saber-toothed cats, cheetahs, mammoths and more. 7. The site was listed as a World Heritage site in 1987. One of the historical monuments of China, it tells the story of a bygone era
Explore China most popular tourist destination with us. Zhoukoudian Archaeological Site In China: Overview,Prominent Features,History,Interesting facts,which is 35.14 km away from China main town, is the most popular destination to add in your travel wishlist.
-
City:
China
-
state:
Beijing
-
country:
China
-
country code:
CN
-
postcode:
102200
Location:
Beijing China

 In China.png)
 In China.png)

 In China.png)