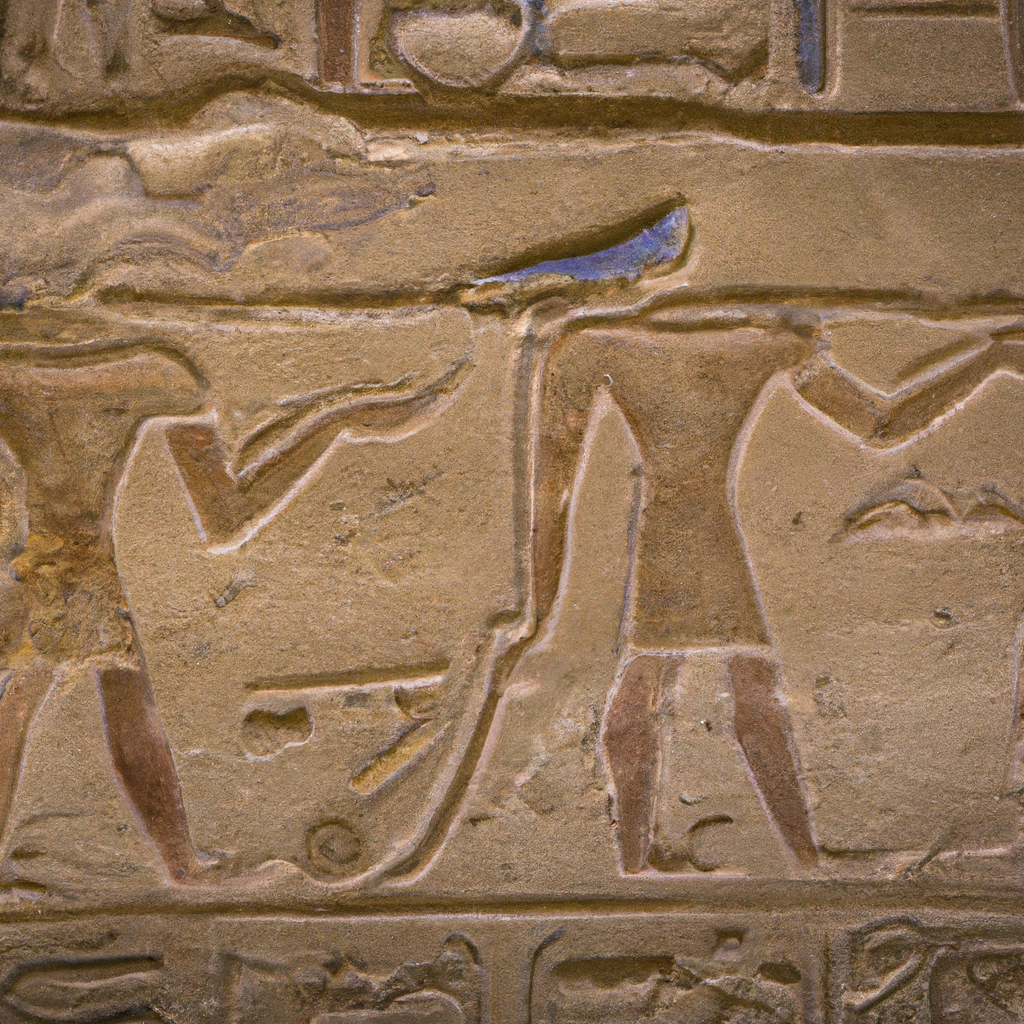Mastaba of Ptahhotep In Egypt: Overview,Prominent Features,History,Interesting facts
Overview:
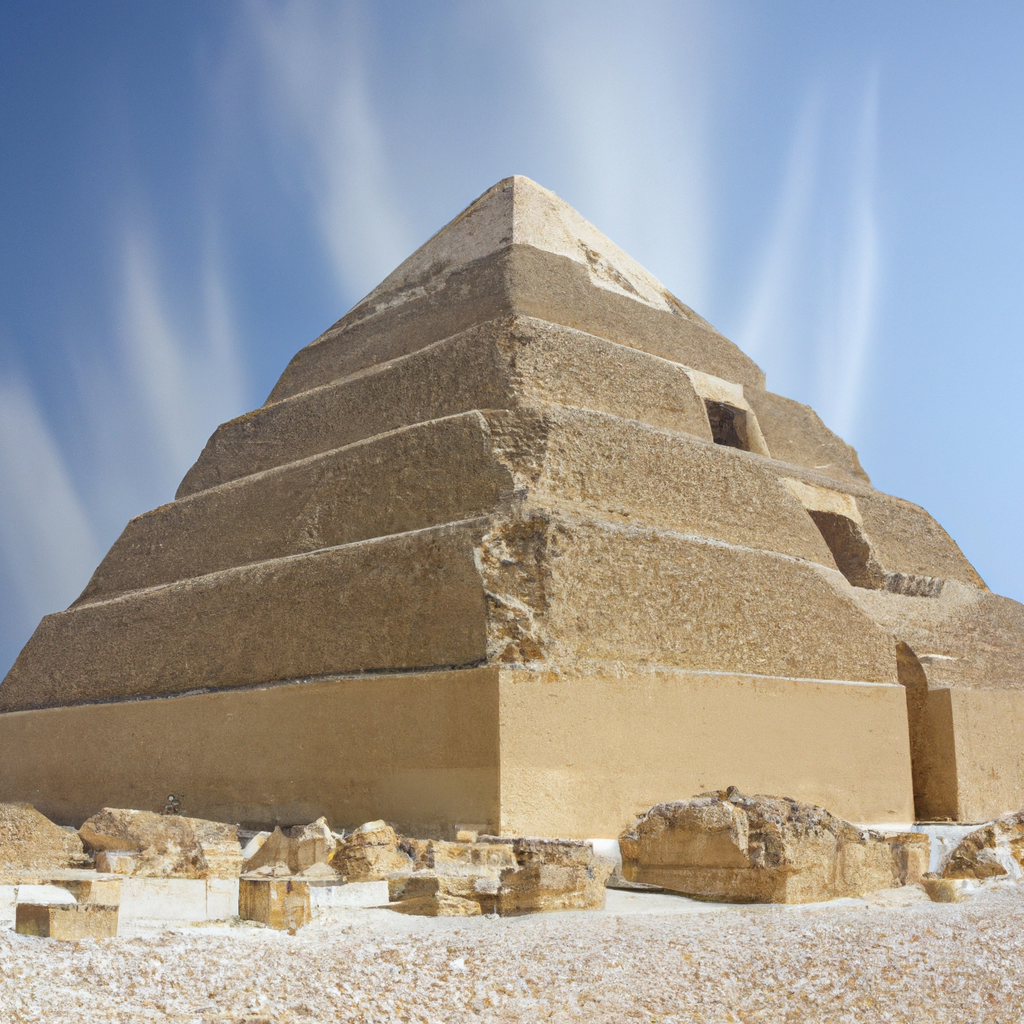
The Mastaba of Ptahhotep is an ancient Egyptian tomb located in Saqqara, Egypt. It contains the remains of Ptahhotep, a high official of the 5th Dynasty (2498-2345 BCE). The mastaba is one of the oldest and the best-preserved tombs in Egypt and is renowned for its unique architecture and beautiful reliefs. It is also an important example of the evolution of tomb construction in ancient Egypt, providing evidence of the transition from mastaba-style tombs to more complex funerary architecture. The mastaba is part of a larger necropolis that includes the Step Pyramid complex of Pharaoh Djoser (2667-2648 BCE). It is one of the most beautiful monuments in Egypt
Prominent Features:
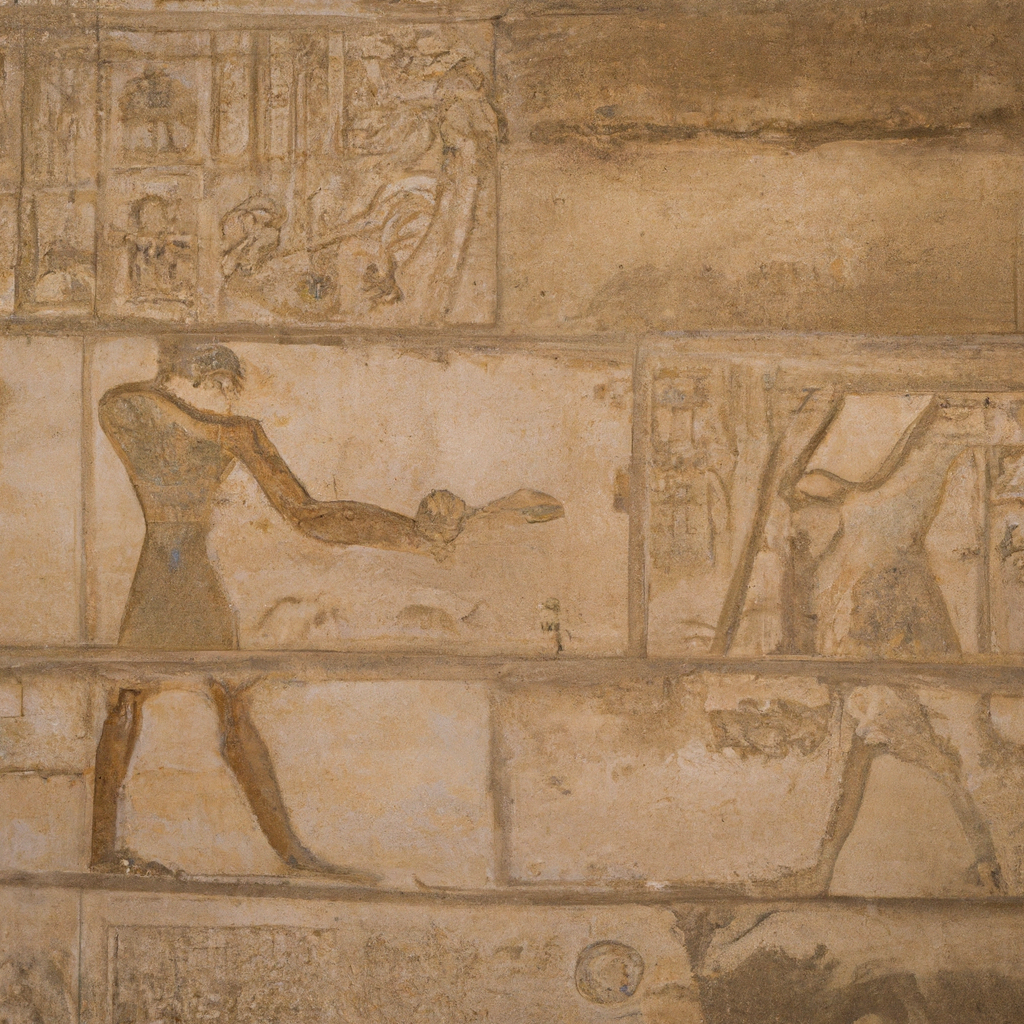
The Mastaba of Ptahhotep in Egypt is a prominent example of a mastaba tomb. It dates back to the 24th Century BCE and is located near the ancient city of Memphis in Egypt. The mastaba is one of the oldest and most elaborate tombs, and is known for its finely carved reliefs. The reliefs depict scenes of hunting, fishing, food preparation, foreign tribute, music, and the presentation of offerings, as well as a scene of the mummification process. The mastaba also features an inscribed autobiography of Ptahhotep, a vizier under the Fifth Dynasty Pharaoh Djedkara Isesi, and a funerary inscription honoring his life. The tomb is believed to have been built for Ptahhotep's son, Ptahhotep II. You can learn history, culture, and heritage through these magnificent monuments in Egypt.
History:
The Mastaba of Ptahhotep is an ancient tomb from the 5th Dynasty of the Old Kingdom of ancient Egypt dating to approximately 2400 BCE. The mastaba is located near Saqqara, near the city of Memphis in northern Egypt, and was discovered accidentally by the French Egyptologist Auguste Mariette in 1850. Excavations at the burial site revealed a subsidiary pyramid, statues, offering chapels and a false door. The Mastaba of Ptahhotep is believed to have been built by the Vizier, Ptahhotep I, who lived during the 5th Dynasty and served under King Isesi or his predecessor Userkaf. His mastaba is one of the earliest recorded examples of funerary architecture in ancient Egypt and is an important source of information about early Egypt's burial practices. The Mastaba of Ptahhotep consists of an aboveground tomb consisting of two levels. On the first level, two false doors lead to two small rooms, each square in shape and lined with mud brick walls topped with a flat stone floor. On the second level, a larger room is believed to be the sarcophagus room where the coffin or mummy was placed. The entrance to the sarcophagus room is adorned with a bas-relief carving of Ptahhotep. The Mastaba of Ptahhotep is also home to a subsidiary pyramid and numerous statues of Ptahhotep and his family, indicating that the tomb was meant to both serve as a memorial to the deceased and offer protection and a continuation of life after death. The grave also contained a number of offering chapels, which were used to make offerings of food and drink in order to sustain and appease the spirit of the deceased in the afterlife. The Mastaba of Ptahhotep is the earliest surviving example of a tomb in Egypt, and its discovery has helped archaeologists and historians to understand the changing cultural practices and burial customs of the Ancient Egyptians. Visit one of the famous monuments of Egypt with your friends and family.
Interesting facts:
1. The Mastaba of Ptahhotep is one of the oldest and most significant works of funerary art from ancient Egypt. 2. The tomb’s architecture is an elite version of a mastaba, featuring a flat roof dome topped by a pyramid. 3. The structure of the tomb suggests that it was built and decorated in the Early Dynastic Period, likely sometime during the end of the 5th dynasty or the beginning of the 6th dynasty. 4. The Mastaba of Ptahhotep was discovered in Saqqara in 1914 and is considered to be one of the oldest known monuments of Egypt. 5. The Mastaba contains the tombs of both Ptahhotep and his son, Ankhhap. 6. The Mastaba also contains a number of jubilees and ritual texts, as well as about five hundred hieroglyphic inscriptions. 7. The Mastaba is considered an important example of early Egyptian funerary art and architecture, as it features a variety of decorative elements. 8. At the time of its discovery, the Mastaba of Ptahhotep was the only surviving early-dynastic structure from Egypt. One of the historical monuments of Egypt, it tells the story of a bygone era
Explore Egypt most popular tourist destination with us. Mastaba of Ptahhotep In Egypt: Overview,Prominent Features,History,Interesting facts,which is 35.14 km away from Egypt main town, is the most popular destination to add in your travel wishlist.
-
City:
Egypt
-
state:
Saqqara
-
country:
EG
-
country code:
Egypt
- postcode:
Location:
Saqqara EG